A gazelle is running at a constant speed of 19.3 m/s toward a motionless hidden cheetah. At the instant the gazelle passes the cheetah, the cheetah accelerates at a rate of 7.1 m/s/s in pursuit of the gazelle. The gazelle maintains its constant speed. By the time the cheetah reaches a speed of 19.3 m/s to match the gazelle, how far apart are the two animals in units of m
Answers
Answer:
the animals are 26.2 meters apart.
Explanation:
Let's define t = 0s as the moment when the cheetah starts accelerating.
The gazelle moves with constant velocity, thus, it is not accelerating, then the acceleration of the gazelle is:
a₁(t) = 0m/s^2
where I will use the subscript "1" to refer to the gazelle and "2" to refer to the cheetah.
for the velocity of the gazelle we just integrate over time to get:
v₁(t) = V0
where V0 is the initial speed of the gazelle, which we know is 19.3 m/s
v₁(t) = 19.3 m/s
To get the position of the gazelle we integrate again:
p₁(t) = ( 19.3 m/s)*t + P0
where P0 is the position of the gazelle at t = 0s, let's define P0 = 0m
p₁(t) = ( 19.3 m/s)*t
The equations that describe the motion of the gazelle are:
a₁(t) = 0m/s^2
v₁(t) = 19.3 m/s
p₁(t) = ( 19.3 m/s)*t
Now let's do the same for the cheetah.
We know that its acceleration is 7.1 m/s^2
then:
a₂(t) = 7.1 m/s^2
for the velocity of the cheetah we integrate:
v₂(t) = (7.1 m/s^2)*t + V0
where v0 is the initial velocity of the cheetah, which we know its zero.
v₂(t) = (7.1 m/s^2)*t
Finally, for the position equation we integrate again, and remember that we have defined the initial position for the gazelle as zero, then the same happens for the cheetah.
p₂(t) = (1/2)*(7.1 m/s^2)*t^2
The equations for the cheetah are:
a₂(t) = 7.1 m/s^2
v₂(t) = (7.1 m/s^2)*t
p₂(t) = (1/2)*(7.1 m/s^2)*t^2
Now, we want to find the distance between both animals when the speed of the cheetah is 19.3 m/s, then first we need to solve:
v₂(t) = (7.1 m/s^2)*t = 19.3 m/s
t = (19.3 m/s)/(7.1 m/s^2) = 2.72s
Now, to find the distance between the two animals, we just compute the difference between the position equations for t = 2.72s
Distance = p₁(2.72s) - p₂(2.72s)
= ( 19.3 m/s)*2.72s - (1/2)*(7.1 m/s^2)*(2.72s)^2
= 26.2 m
So the animals are 26.2 meters apart.
Related Questions
what is the maximum efficiency that a heat engine could have when operating between the normal boiling and freezing temperatures of water

Answers
The maximum efficiency that a heat engine could have when operating between the normal boiling and freezing temperatures of water is 26.8 %
η = ( \(T_{H}\) - \(T_{C}\) ) / \(T_{H}\) * 100
η = Efficiency
\(T_{H}\) = Hottest temperature
\(T_{C}\) = Coldest temperature
Hottest temperature = Boiling point
Coldest temperature = Freezing point
\(T_{H}\) = 100 °C = 373 K
\(T_{C}\) = 0 °C = 272 K
η = ( 373 - 273 ) / 373 * 100
η = 100 / 373 * 100
η = 26.8 %
In a heat engine, the heat energy is converted into mechanical energy which will be used to do mechanical work like pushing a piston out from the cylinder.
Therefore, the maximum efficiency that a heat engine could have when operating between the normal boiling and freezing temperatures of water is 26.8 %
To know more about maximum efficiency of a heat engine
https://brainly.com/question/25289326
#SPJ1
Some plants disperse their seeds when the fruit splits and contracts, propelling the seeds through the air. The trajectory of these seeds can be determined with a high-speed camera. In an experiment on one type of plant, seeds are projected at 20 cm above ground level with initial speeds between 2.3 m/s and 4.6 m/s. The launch angle is measured from the horizontal, with +90∘ corresponding to an initial velocity straight up and -90∘ straight down. The experiment is designed so that the seeds move no more than 0.20 mm between photographic frames. What minimum frame rate for the high-speed camera is needed to achieve this?
a. 250 frames/s
b. 2500 frames/s
c. 25,000 frames/s
d. 250,000 frames/s.
Answers
Answer:
c. 25,000 frames/s
Explanation:
For computing the minimum frame rate for high speed first we have to determine the time by applying the following equation
\(t = \frac{d}{s}\)
\(= \frac{0.2\ mm}{4.6\ m/s }\)
\(= \frac{0.2 \times 10 ^{-3}}{4.6\ m/s }\)
\(= 4.347 \times 10^{-5} sec\)
Now the frame rate is
\(Frame\ rate = \frac{1}{t}\)
\(= \frac{1}{4.347 \times 10^{-5} sec}\)
= 23,000 frame per sec
≈ 25,000 frame per sec
First we have find the time then after finding out the time we calculate the frame time by applying the above formula so that the minimum frame rate could come
If you pull with a constant force of 400n , how much mechanical work does it take to pull pinball launcher back 0.2meters
Answers
If you pull with a constant force of 400 N for 0.2 meters, then the work done will be equal to 80 J.
What is Work?In physics, the word "work" involves the measurement of energy transfer that takes place when an item is moved over a range by an externally applied, at least a portion of which is applied within the direction of the displacement.
The length of the path is multiplied by the element of a force acting all along the path to calculate work if the force is constant. The work W is theoretically equivalent towards the force f times the length d, or W = fd, to portray this concept.
As per the given information in the question,
Force, f = 400 N
Displacement, d = 0.2 meters
\(Work done(W)=Force(f)*Displacement(d)\)
W = 400 × 0.2
W = 80 J.
To know more about Work:
https://brainly.com/question/13662169
#SPJ1
Two identical conducting sphere, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.108 N when their center-to-center separation is 50.0 cm. The sphere are then connected by a thin conducing wire. When the wire is removed, the sphere repel each other with an electrostatic force of 0.0360 N. Of the initial charges on the sphere, with a positive net charge, what was the negative charge on one of them?
Answers
The negative charge on one of the identical spheres in a pair of conducting, fixed, and attracted to each other by an electrostatic force spheres is -1.00*10^-6 C. We can calculate this using Coulomb's law.
We can begin by using Coulomb's law, which states that the electrostatic force between two charges is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Coulomb's law can be mathematically written as:
F = k * (q1 * q2) / r^2
where F is the force, k is the Coulomb constant, q1 and q2 are the charges on the two spheres, and r is the distance between their centers.
Given that the force of attraction is 0.108 N when the spheres are 50.0 cm apart, we can use the Coulomb's law to find the product of the charges on the spheres.
0.108 N = (9 * 10^9 N*m^2/C^2) * (q1 * q2) / (0.50 m)^2
The product of the charges on the two spheres is q1q2 = (0.108 N * (0.50 m)^2) / (9 * 10^9 Nm^2/C^2) = 1.2 * 10^-7 C^2
We can use this value to find the charges on the spheres when they are connected by a thin conducting wire and repelling each other with an electrostatic force of 0.0360 N.
0.0360 N = (9 * 10^9 N*m^2/C^2) * (q1 * q2) / (0.50 m)^2
q1q2 = (0.0360 N * (0.50 m)^2) / (9 * 10^9 Nm^2/C^2) = 4.0 * 10^-8 C^2
Since the product of the charges q1*q2 is now smaller, we can assume that one of the charges (let's say q1) is now smaller and the other charge (q2) is now bigger, hence have opposite charges.
We can use the formula q1q2 = 1.210^-7 C^2 / 4.0*10^-8 C^2 = 3q1q2
q2 = 3q1 and q1q2 = 4*10^-8 C^2
Substituting, we get q1 = (410^-8 C^2) / 3q1 = 1.3310^-8 C
The negative charge on one of the sphere is 1.33*10^-8 C
Learn more about Coulomb's law:
https://brainly.com/question/506926
#SPJ4
Think of pushing a heavy object to make it slide across the floor (like a big, heavy box with
no wheels on it). Assuming the object is initially at rest on the floor, compare the force you
need to start the object moving to the force you need to keep the object moving after it has
started to slide.
Answers
Answer:
heavy box with no heels on it
Make a poem about waves with 12 Lines and 3 Stanzas.
Answers
In a ocean full of storms
A new wave was born
Deep into that darkness flooding
Suddenly, I heard some pummeling
By the grave I saw the winds
And the sun just shined
Answer:
a friendly face that comes with waves,
the waves of all the memorial days,
and with these days we smile with pride,
as for the waves we used to ride,
given up the day has passed,
how it went away like an hour glass,
as if we knew the world was right,
just like the waves, oh so bright,
the time has come the days have passed,
the waves ashore the waves alast,
as if the friendly face was right,
the waves that rode, oh goodnight.
27. CHALLENGE The car in Figure 16 travels west with a forward acceleration of 0.22 m/s2. What was the car's velocity (v) at point x if it travels a distance of 350 m in 18.4 s?
Vi = ? x x Figure 16
Answers
The car's velocity (v) at point x, if it travels a distance of 350 m in 18.4 s is 12.41m/s
According to the equation of motions;
v² = u² + 2as
Given that
v is the final velocity
u is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration
s is the distance
Given the following parameters
u = 0m/s
a = 0.22m/s²
s = 350m
Susbstitute the given values into the formula
v² = 0² + 2(0.22)(350)
v² = 154
v = √154
v = 12.41 m/s
Hence the car's velocity (v) at point x, if it travels a distance of 350 m in 18.4 s is 12.41m/s
Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/20352766
Usain Bolt is wicked fast. In fact, he is the fastest human in the world and
ran at a crazy 10.1 m/s in the Olympic Games. What is his mass if he had
9.890 Joules of kinetic energy in that race?
Answers
Explanation:
KE = (1/2)mv^2 ---> m = 2KE/v^2 = 2(9.890 J)/(10.1 m/s)^2
= 0.194 kg
Note: I think there's something wrong with the energy value given. The mass value for Usain Bolt is too small. That's less than a pound!
Inelastic
In a railroad yard, a train is being assembled. An empty boxcar, coasting at 3 m/s, strikes a car
that is stationary, and the cars couple together. Each of the boxcars has a mass of 9000 kg when
empty. What is the velocity after the cars are coupled together?
Equation: m1 (v1) + m2 (v2) = (m1 + m2)
M1 = 9000 kg v1 = 3 m/s M2 = 9000 kg v2 = 0m/s
V' =
Answers
The velocity of the cars after they are coupled together, given that they both have masses of 9000 Kg, is 1.5 m/s
How do I determine the velocity of the cars after they are coupled together?First, we shall list out the given parameters from the question. This is shown below:
Mass of first car (m₁) = 9000 KgInitial velocity of first car (u₁) = 3 m/sMass of second car (m₂) = 9000 KgInitial velocity of of second car (u₂) = 0 m/sFinal velocity of cars (v) = ?The velocity of the cars after they are coupled together can be obtained as illustrated below:
m₁u₁ + m₂u₂ = v(m₁ + m₂)
(9000 × 3) + (9000 × 0) = v(9000 +9000)
27000 + 0 = 18000v
27000 = 18000v
Divide both sides by 18000
v = 27000 / 18000
v = 1.5 m/s
Thus, the velocity of the cars after collision is 1.5 m/s
Learn more about velocity after collison:
https://brainly.com/question/28151651
#SPJ1
What are patients most likely to prepare as part of their right to make decisions about end of life care under federal legislation
Answers
Monitoring cash flow and keeping track of the bottom line of a business are responsibilities for whom?
Answers
A financial manager.
Explanation:
This is because a financial manager oversees the financial operations of a company. Generally, a financial manager assumes accounting responsibilities for the company. A financial manager is responsible for planning and managing the company's financial resources.
Side note:
Hope this helps!
Please give Brainliest!
A student in the Biomechanics class has decided that she would like to make her arms
stronger. She has a mass of 63 kg, She chooses to complete some elbow flexion exercises
using a kettlebell. For this problem, consider the hand and forearm to be a single segment.
The distance from her elbow to her wrist is 22.86 cm.
The force from the kettlebell is applied to her hand, which is 30.48 cm from her elbow joint.
She knows that the moment arm of the elbow extensor muscles about the elbow axis is
Answers
Answer:
what is heat and transfer
Please help! Also Show your work!!!

Answers
As a result, 0.56 A of current is flowing through the tracks.
What kind of current does a railway track have?Railway electrification in nations where 60 Hz is the standard grid power frequency uses a 25 kV at 60 Hz voltage.
To determine the current flowing through the tracks, we can apply Ohm's law: I = V / R
where the variables I, V, and R stand for current, voltage, and resistance, respectively.
Inputting the specified values results in:
I = 25 V / 45 Ω
I = 0.56 A
To know more about current visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/10439697
#SPJ1
Initial velocity: U = ?
Final velocity: v = 0
Gravity: g = 9,8 ms²
Height: h = 20m
v² = u² + 2gh
0 = u² + 2 (-9,8ms²) x 20m
Answers
The initial velocity of the object in motion is determined as 19.8 m/s.
What is the initial velocity of the object?The initial velocity of the object in motion is calculated by applying the third equation of motion as follows;
v² = u² + 2gh
where;
v is the final velocity of the objectu is the initial velocity of the objectg is acceleration due to gravityh is the height through which the object riseswhen the object reaches maximum height, the final velocity, v = 0
The initial velocity of the object in motion is calculated as;
0 = u² + 2 (-9,8ms²) x 20m
0 = u² - 392
u² = 392
u = √392
u = 19.8 m/s
Learn more about initial velocity here: https://brainly.com/question/19365526
#SPJ1
A bullet is fired horizontally from a gun. At the same time a similar bullet is dropped from the
same height. The fired bullet will:
a) hit the ground first
b) hit at the same time as the dropped bullet
c) hit the ground second
d) never hit the ground
record final answer
Answers
The fired bullet will: hit the ground second.
option C is the correct answer.
What is vertical velocity?
The vertical velocity of an object is the velocity of the object along the y axis.
The vertical velocity of an object decreases as the moves upwards, and eventually becomes zero at the maximum height due to the influence of acceleration due to gravity.
As the object begins to descend, the vertical velocity starts to in increase and eventually becomes maximum before the object hits the ground.
The horizontal velocity of an object remains constant because it is not affected by acceleration due to gravity in the horizontal direction.
Thus, the bullet fired from a gun will travel longer distance than the bullet dropped from same height due to influence of gravity.
Learn more about vertical velocity here: https://brainly.com/question/24949996
#SPJ1
A satellite is orbiting the earth. If a payload of material is added until it doubles the satellite's mass, the earth's pull of gravity on this satellite will double but the satellite's orbit will not be affected. A satellite is orbiting the earth. If a payload of material is added until it doubles the satellite's mass, the earth's pull of gravity on this satellite will double but the satellite's orbit will not be affected. True False
Answers
Answer:
it is True
Explanation:
I hope this helps
The figure below shows a ball resting on a frictionless track at position A.
The ball has a mass of 20 kg and is released from position A, the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s. How much kinetic energy will the ball have at position B?

Answers
To find the kinetic energy at position B, we need to know the height or the velocity at position B. Without this information, we cannot calculate the exact value of the kinetic energy.
To determine the kinetic energy of the ball at position B, we need to consider the m conservation of Mechanical energy. Since the ball is released from position A, we can assume that there is no initial kinetic energy (velocity is zero), and the total mechanical energy at position A is equal to the potential energy.
The potential energy at position A can be calculated using the formula:
Potential energy at A = mass * gravitational acceleration * height
Potential energy at A = 20 kg * 9.8 m/s² * height
Now, at position B, all the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. The kinetic energy at position B is given by the formula:
Kinetic energy at B = 1/2 * mass * velocity²
Since the ball is released from rest, the velocity at position B can be determined using the conservation of mechanical energy:
Potential energy at A = Kinetic energy at B
20 kg * 9.8 m/s² * height = 1/2 * 20 kg * velocity²
Simplifying the equation, we get:
9.8 m/s² * height = 1/2 * velocity²
for more questions on kinetic energy
https://brainly.com/question/20658056
#SPJ8
Match the part of the diagram to its correct label.

Answers
Answer:
Hope it helps you
Explanation:
1. Nucleus
2. Proton
3. Electron
4. Neutron
PLS RATE AS BRAINLIEST ANSWER
Problem 3 A small ball is launched at an angle of 30.0 degrees above the horizontal. It reaches a maximum height of 2.5 m with respect to the launch position. Find (a) the initial velocity of the ball when it’s launched and (b) its range, defined as the horizontal distance traveled until it returns to his original height. As always you can ignore air resistance.(a) Initial velocity[Hints: How is v0 related to vx0 and vy0. How can you use the information given to calculate either or both of the components of the initial velocity?](b) Range[Hints: This problem is very similar to today’s Lab Challenge except that for the challenge the ball will land at a different height.]

Answers
a)
In order to find the initial velocity of the ball, we can use the formulas below:
\(\begin{gathered} v_{y0}=v_0\cdot\sin (\theta) \\ v^2_y=v^2_{y0}+2\cdot g\cdot d \end{gathered}\)At the maximum height, the vertical speed is zero. So, using theta = 30°, d = 2.5 m and vy = 0, we have:
\(\begin{gathered} v^2_y=v^2_{y0}+2\cdot g\cdot d \\ 0^2=v^2_{y0^{}}+2\cdot(-9.8)\cdot2.5 \\ v^2_{y0}=49^{} \\ v_{y0}=7 \\ \\ v_{y0}=v_y\cdot\sin (\theta) \\ 7=v_y\cdot\frac{1}{2} \\ v_y=14\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}\)b)
To find the range, let's calculate the horizontal component of the velocity and the time of flight:
\(\begin{gathered} v_x=v\cdot\cos (\theta)_{} \\ v_x=14\cdot\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2} \\ v_x=12.124\text{ m/s} \\ \\ v_y=v_{y0}+g\cdot t \\ 0=7-9.8\cdot t \\ t=\frac{7}{9.8} \\ t=0.714 \\ \\ t_f=2t=1.43\text{ s} \\ \\ d_x=v_x\cdot t \\ d_x=12.124\cdot1.43 \\ d_x=17.34\text{ m} \end{gathered}\)A piston above a liquid in a closed container has an area of 0.75m^2, and the piston carries a load of 200kg. What will be the external pressure on the upper surface of the liquid?
Answers
Answer:
2613.3 pa
Explanation:
p=F/A
p=ma/A
p=200×9.8/0.75
p=2613.3
How many seconds are in 28 hours?
Answers
Answer:
1680 seconds
Explanation:
\(28 hrs * \frac{60 s}{1 hr} =1680s\)
Please help. 25 POINTS, PLEASE ANSWER PROMPTLY
If an object has a velocity of 0 m/s, deceive its motion:
A. It's not moving
B. It's moving slower
C. It's moving faster
D. It's moving at the same rate
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
11. [0/10 Points]
A rectangular block has dimensions 2.9 cm x 2.6 cm x 10.0 cm. The mass of the block is 605.0 g
What is the volume of the block?
4.0
DETAILS
x cm³
What is the density of the block?
4.0
X g/cm³
Submit Answer
PREVIOUS ANSWERS
Answers
Volume of rectangular block is 75.4 cm^3
Density of the rectangular block is 8.02 g/cm^3
Volume is simply defined as the space occupied within the boundaries of an object in three-dimensional space.
It is also known as the capacity of the object.
Volume of rectangular block = length× breadth× height
=2.9 cm × 2.6 cm × 10.0 cm
=75.4 cm^3
Density is defined as the substance's mass per unit of volume.
Mathematically ,density is defined as mass divided by volume.
Density of the block = Mass of block / volume of block
=605.0 g / 75.4 cm^3
=8.02 g/cm^3
To know more about the density here
https://brainly.com/question/6107689
#SPJ1
How do you get c and d?
A positive charge of magnitude Q1 = 0.85 nC is located at the origin. A negative charge Q2 = −7.5 nC is located on the positive x-axis at = 15.5 cm from the origin. The point P is located at = 6.5 cm above the charge Q2.
a) Sketch the directions of Q1, Q2, and on the figure. Make sure to label your arrows.
b) Determine the magnitudes of E1 and E2 at point P.
c) Determine the x and y components of E1 at point P.
d) Determine the x and y components of E2 at point P.
e) Determine the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at point P due to the two charges.
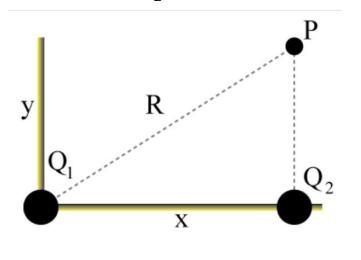
Answers
Answer:
of the net electric field at point P due to the two charges.
Explanation:
Two forces F1 = -6.00i + 7.90j and F2 = 6.80i + 5.30j are acting on an object with a mass of m = 4.10 kg. The forces are measured in newtons, i and j are the unit vectors. What is the magnitude of the object's acceleration?
Answers
The magnitude of object's acceleration is 3.26m/s².
The mass of the body is 4.10 lg.
The two forces that are acting on the object are F₁ = -6i + 7.9j newton and F₂ = 6.8i + 5.3j Newton.
We know that the force acting on an object is,
F = Ma
Where,
F is the force acting,
M is the mass of the object and,
a is the acceleration of the object.
As we can see, two forces are acting on the body,
We can simplify the forces in x direction and y direction,
The forces are F₁ = -6i + 7.9j N and F₂ = 6.8i + 5.3j N.
So, the total force in x-direction,
Fₓ = (-6+6.8)i
Fₓ = 0.8i
Fᵧ = (7.9+5.3)j
Fᵧ = 13.2j
So, the net force Fₙ on the object is Fₙ = (0.8i + 13.2j) N
Now, putting value of force and mass in the formula,
F = Ma
0.8i + 13.2j = 4.1a
a = 0.19i + 3.21j m/s².
The magnitude of acceleration is,
|a| = √[(0.19)²+(3.21)²]
|a| = 0.361 +10.3
|a| = 3.26m/s².
So, the magnitude of acceleration is 3.26m/s².
To know more about Force, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/12970081
#SPJ9
find the dimension for velocity
Answers
Two blocks, 1 and 2, are connected by a massless string that passes over a massless pulley. 1 has a mass of 2.25 kg and is on an incline of angle 1=42.5∘ that has a coefficient of kinetic friction 1=0.205. 2 has a mass of 5.55 kg and is on an incline of angle 2=33.5∘ that has a coefficient of kinetic friction 2=0.105
. The figure illustrates the configuration.
A system of two blocks connected by a rope passing over a pulley. The system sits atop a scalene triangle whose long edge forms the base. The pulley is attached to the apex of the triangle. Box M subscript 1 rests on the triangle edge to the left of the pulley, which makes an angle of theta subscript 1 with the base of the triangle. The coefficient of friction between box M sub 1 and the surface is mu subscript 1. Box M subscript 2 rests on the triangle edge to the right of the pulley, which makes an angle of theta subscript 2 with the base of the triangle. The coefficient of friction between box M sub 2 and the surface is mu subscript 2.
Answers
The force acting on the system of two blocks connected by a rope passing over a pulley is -13.26 N.
The system of two blocks connected by a rope passing over a pulley are M1 and M2, where M1 rests on the triangle edge to the left of the pulley, which makes an angle of theta subscript 1 with the base of the triangle. The coefficient of friction between box M1 and the surface is mu subscript 1. M2 rests on the triangle edge to the right of the pulley, which makes an angle of theta subscript 2 with the base of the triangle.
The coefficient of friction between box M2 and the surface is mu subscript 2. The system sits atop a scalene triangle whose long edge forms the base. The pulley is attached to the apex of the triangle.M1 has a mass of 2.25 kg and is on an incline of angle 1=42.5∘ that has a coefficient of kinetic friction 1=0.205. M2 has a mass of 5.55 kg and is on an incline of angle 2=33.5∘ that has a coefficient of kinetic friction 2=0.105.The free-body diagram of M1 shows that the weight of M1 acts straight downwards (vertically) and the normal force acts perpendicular to the slope.
The force of friction opposes the motion and acts opposite to the direction of motion.M1 = 2.25 kgTheta subscript 1 = 42.5 degreesMu subscript 1 = 0.205g = 9.81 m/s²In the free-body diagram of M2, the normal force acts perpendicular to the incline of the slope, the weight of the object acts vertically downwards and parallel to the incline, and the force of friction opposes the motion and acts opposite to the direction of motion.M2 = 5.55 kgTheta subscript 2 = 33.5 degreesMu subscript 2 = 0.105g = 9.81 m/s²The tension in the string is the same throughout the rope. Since the masses are being pulled by the same rope, the acceleration of the objects is the same as the acceleration of the rope.
The tension in the string is directly proportional to the acceleration of the objects and the rope.A system of two blocks connected by a rope passing over a pulley has a total mass of M. The acceleration of the system is given by the formula below:a = [(m1-m2)gsin(θ1) - μ1(m1+m2)gcos(θ1)] / (m1 + m2)Where, μ1 = 0.205 is the coefficient of friction of block M1θ1 = 42.5 degrees is the angle of the incline of block M1M1 = 2.25 kg is the mass of block M1M2 = 5.55 kg is the mass of block M2g = 9.81 m/s² is the acceleration due to gravitysinθ1 = sin 42.5 = 0.67cosθ1 = cos 42.5 = 0.75The acceleration of the system is:a = [(2.25-5.55)(9.81)(0.67) - (0.205)(2.25+5.55)(9.81)(0.75)] / (2.25 + 5.55)a = -1.7 m/s² (the negative sign indicates that the system is accelerating in the opposite direction).
The force acting on the system is given by:F = MaWhere M is the total mass of the system and a is the acceleration of the system. The total mass of the system is:M = m1 + m2M = 2.25 + 5.55M = 7.8 kgThe force acting on the system is:F = 7.8(-1.7)F = -13.26 N (the negative sign indicates that the force is acting in the opposite direction).
for more question on force
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ8
A cannon fires a cannonball directly upward at 300 m/s. How long (in s) does the cannonball move upward before stopping?
Answers
The time taken for the cannonball to move upward before stopping, given that is was fired directly upward at 300 m/s is 30.6 seconds
How to I determine the time?Velocity and time are related according to the following equation of motion
v = u + gt
Where
v is the final velocityu is the initial velocityg is the acceleration due to gravityt is the timeFrom the question given above, the following data were obtained:
Initial velocity (u) = 300 m/sFinal velocity (v) = 0 m/sAcceleration due to gravity (g) = 9.8 m/s²Time taken to stop (t) = ?The time taken for the cannonball to move upward before stopping can be obtained as illustrated below:
v = u - gt (since the ball is going against gravity)
0 = 300 - (9.8 × t)
0 = 300 - 9.8t
Collect like terms
-9.8t = 0 - 300
-9.8t = -300
Divide both sides by -9.8
t = -300 / -9.8
t = 30.6 seconds
Thus, the time taken is 30.6 seconds
Learn more about time:
https://brainly.com/question/14195937
#SPJ1
Which has a bigger impact on force charge or distance explain and use Coulomb’s law why
Answers
Explanation:
Distance has a bigger impact on force than charge according to Coulomb's law.
Coulomb's law states that the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically, this is represented as:
F = k(q1 x q2) / d^2
where F is the force between the two charges, q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, d is the distance between the charges, and k is a constant.
This means that as the distance between two charged objects increases, the force of attraction or repulsion between them decreases rapidly. Conversely, as the distance between them decreases, the force increases rapidly. On the other hand, the magnitude of charge affects the force of attraction or repulsion, but not as significantly as the distance. Therefore, distance has a bigger impact on force than charge.
A constant force is applied to an object, causing the object to accelerate at 9.0 m/s2 . What will the acceleration be if the force is doubled?
Answers
When the constant force applied to an object, causing an acceleration of 9.0 m/s², is doubled, the final acceleration is also doubled.
The acceleration is related to the force by Newton's second law:
\( F = ma \)
Where:
F. is the force applied
m: is the object's mass
a: is the acceleration
For the first case, when a constant force is applied and the acceleration is 9.0 m/s², we have:
\( F_{1} = ma_{1} = 9m \) (1)
Now, when the force is doubled:
\( F_{2} = ma_{2} \)
\( 2F_{1} = ma_{2} \)
\( a_{2} = \frac{2F_{1}}{m} = \frac{2*9m}{m} = 18 m/s^{2} \)
Therefore, when the force doubles, the acceleration also doubles.
To find more about Newton's second law, go here: https://brainly.com/question/23845187?referrer=searchResults
I hope it helps you!