Calculate the amount of heat needed to boil 132.g of water (H20), beginning from a temperature of 7.4 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol
Answers
62.297 kJ of heat is required to boil 132.g of water (H20), beginning from a temperature of 7.4 °C.
The quantity of heat required to boil 132 g of water at a temperature of 7.4°C is to be calculated. The heat energy required to increase the temperature of a material by one degree Celsius is referred to as heat capacity or specific heat. The formula for specific heat capacity is given by Q = mCΔT where Q is the quantity of heat, m is the mass of the material, C is the specific heat capacity of the material, and ΔT is the difference in temperature.
We'll utilise the following formula to calculate the heat required:q = m x c x ΔT + m x Lwhere q is the quantity of heat, m is the mass of the material, c is the specific heat of the material, ΔT is the difference in temperature, and L is the material's latent heat of vaporization.
The value of q can now be calculated : q = (132.0 g) × (4.184 J/g°C) × (100°C – 7.4°C) + (132.0 g) × (2.26 × 106 J/kg)q = 62297.0 J. The heat required to boil 132 g of water beginning at 7.4°C is 62297.0 J. This means that 62.297 kJ of heat is required.
Know more about specific heat capacity here:
https://brainly.com/question/29766819
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Can you explain what the boundaries are (6th grade science)
Answers
Answer:
Personal boundaries or the act of setting boundaries is a life skill that has been popularized by self help authors and support groups since the mid 1980s. It is the practice of openly communicating and asserting personal values as way to preserve and protect against having them compromised or violated.
I have an unknown quantity of gas in 31.0 L at 260 mmHg and 87°C, how many moles of gas do I have
A 1.48 moles
B 0.36 moles
C 22.4 moles
D. 273 moles

Answers
Answer: B. 0.36 moles
Explanation:
According to ideal gas equation:
\(PV=nRT\)
P = pressure of gas = 260 mm Hg = 0.342 atm (760 mm Hg= 1atm)
V = Volume of gas = 31.0 L
n = number of moles = ?
R = gas constant =\(0.0821Latm/Kmol\)
T =temperature =\(87^0C=(87+273)K=360K\)
\(n=\frac{PV}{RT}\)
\(n=\frac{0.342atm\times 31.0L}{0.0821L atm/K mol\times 360K}=0.36moles\)
Thus the moles of gas present are 0.36
what is the density of a gas at STP that has a molar mass of 50.0 g/mol?
Answers
Answer:
2.232 g/L
Explanation:
Assuming 1 mol, volume at STP is 22.4 L so you simply divide 50g by 22.4 L to get density
The density of the given gas is required.
The density of the gas at STP is 2.232 g/L.
M = Molar mass of gas = 50 g/mol
1 mole of any gas at STP occupies 22.4 L.
V = Volume per mole = 22.4 L/mol
Density is given by
\(\rho=\dfrac{M}{V}\\\Rightarrow \rho=\dfrac{50}{22.4}\\\Rightarrow \rho=2.232\ \text{g/L}\)
Learn more:
https://brainly.com/question/8684338
https://brainly.com/question/12247942
Complete the following radioactive decay problem. Please help

Answers
Answer:
230 90Th
Explanation:
A careful observation of the equation given in question shows that 234 92U is undergoing alpha decay. This means that the resulting daughter nuclei will have a decrease of 4 in the mass number and a decrease of 2 in the atomic number.
Please see attached photo for further details.
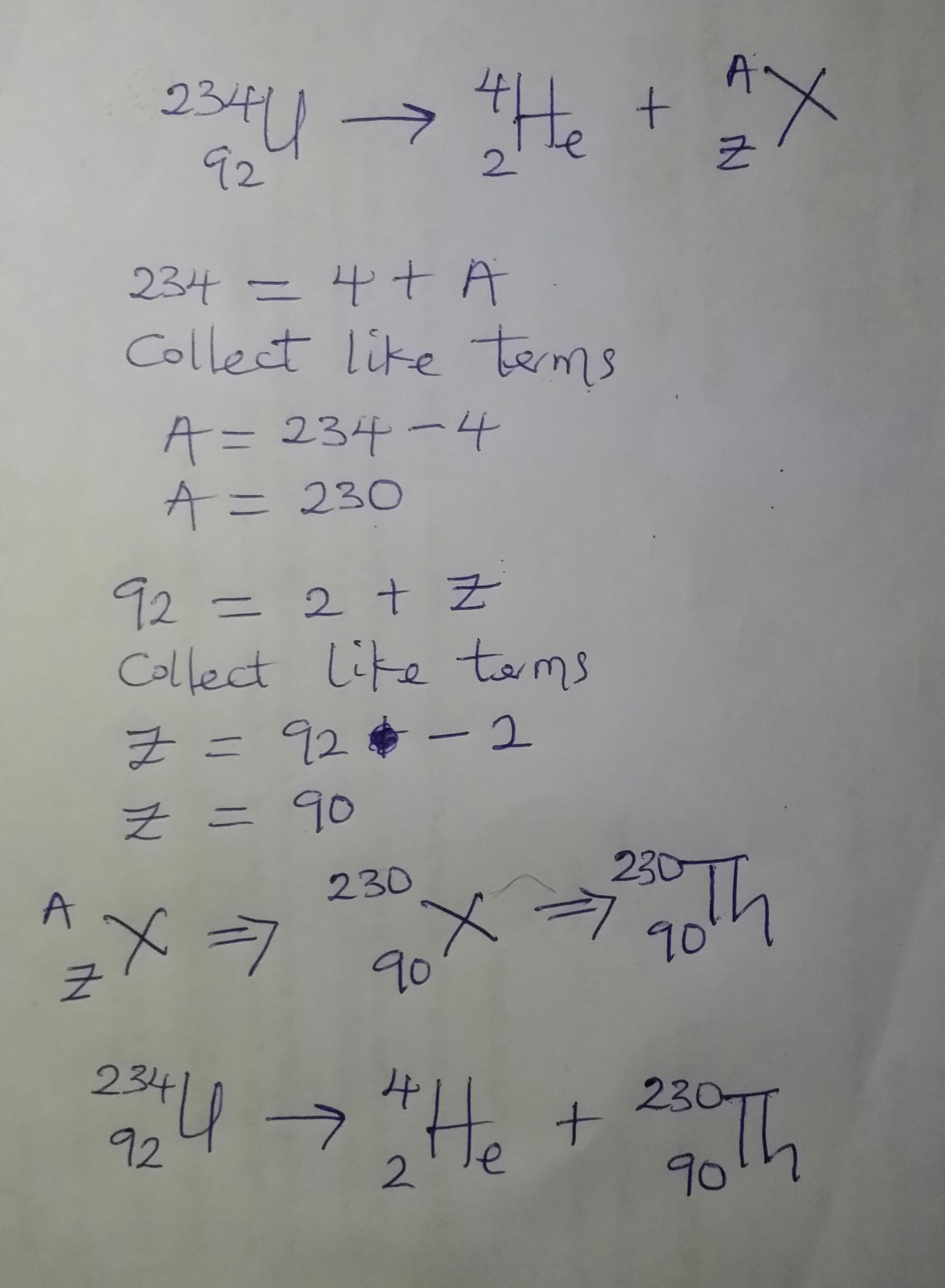
Part B Think about the design that worked the best. Could you improve the best design and raise its internal temperature? Think about what materials you could use to improve the design. Here are some things to consider: How does the size of the reflective surface affect the temperature of the oven? Would insulating the oven help it retain heat, or would more heat be lost? Would a tighter or a looser cover heat the oven faster? How about no covering at all? Describe how you plan to improve the efficiency of the best oven design.
Answers
Answer:
One reason for Jennelle's designs working better is because her aluminum foil sunlight reflector was larger. So. the size of the reflective surface does affect the temperature of the oven. For any given design, the larger the insolated area, the greater the power. Meaning a smaller cooker only collects a small amount of sunlight; no matter how good the design.
That is one reason why the parabolic solar oven design works so well. Parabolic solar cookers use a parabolic-shaped reflector to direct sunlight to a small area in order to generate heat for cooking. They are able to reach temperatures as high as 400°F.
Insulating the oven would help it retain heat. Insulation lets you collect more heat and light energy, which allows you to raise the temperature to even higher levels. So, insulation is anything that lets you "hold on to" that collected heat and lose less of it.
A tighter cover would heat the oven faster rather than a looser cover. The parabolic design doesn't have a cover, although the food itself is usually in a pot or container.
Explanation:
In most designs, using a tighter cover and increasing the reflecting surface will both raise the temperature. Insulation will, however, typically lower the temperature.
What does it mean to design a product ?It is frequently necessary to add, remove, or adjust elements while designing a product in order to increase its efficiency. The temperature and how to raise or lower it is among the aspects taken into account in items like ovens.
Some methods for raising the temperature include:
Increasing the reflecting surface will raise the temperature of the product since reflective surfaces reflect both light and heat.Tighter cover: Raising the temperature by removing any places where heat can escape, such by using a tighter cover.Insulation: Since insulation is primarily employed to disrupt the cycle of heat transfer, applying insulation typically entails lowering the product's internal temperature or concentrating the heat in a single location.
Thus, In most designs, using a tighter cover and increasing the reflecting surface will both raise the temperature.
To learn more about temperature, follow the link;
https://brainly.com/question/11464844
#SPJ2
What factors might affect the amount of energy needed for
evaporation to occur and account for any differences between the temperatures
you observed?
Answers
6 important factors that affect evaporation are : 1. Wind assists evaporation; for example in clothes dry faster under a fan. 2. Heat assists evaporation; for example, in summer clothes dry faster than in winter.
Now have a free meme

Use VSEPR theory to predict the bond angles in a molecule of methane (CH4), which is a covalently bonded molecule.
Answers
Answer:
109.5 Degrees
Explanation:
Because CH4 is sp4 hybridized (Carbon is bonded to the 4 Hydrogens), the geometry of the molecule must be tetrahedral. Tetrahedral moleculues have bond angles of 109.5 Degrees.
From the list provided below, choose those observations that accurately describe the mineral presented in this image.This mineral has a metallic luster.
This mineral is opaque, meaning that it is not clear; light does not pass through it.
This mineral has cleavage.
Answers
The mineral presented in the image has a metallic luster. It is opaque, which means that it is not clear and light does not pass through it. It also has cleavage, which refers to the tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weakness.
The cleavage is evident in the image, as the mineral appears to have flat, smooth surfaces that intersect at sharp angles when it is broken or fractured.Cleavage is one of the most important properties of a mineral because it provides information about the way in which the mineral will break when subjected to external forces.
A mineral with good cleavage will break into pieces that have a smooth, flat surface, while a mineral with poor cleavage will break into pieces that have an uneven surface. This property is often used by mineralogists to help identify minerals since it is unique to each mineral.
To learn more about metallic luster, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/1828077
#SPJ11
The mineral’s luster, opacity, and cleavage define its properties. Metallic luster means it reflects light like metal, opacity implies no light passes through it, and cleavage speaks to how it breaks.
Explanation:In order to determine the characteristics of a mineral, we assess attributes such as the mineral's luster, opacity, and cleavage. The metallic luster refers to how light interacts with the surface of a mineral, metallic luster means the mineral reflects light as a polished metal would.
When a mineral is opaque, it means that light does not pass through it at all - it is not transparent or translucent. Lastly, a mineral's cleavage refers to how it breaks or fractures along distinctive planes. To accurately describe the mineral in the image, these three characteristics would need to be observable.
Learn more about Mineral refer here:https://brainly.com/question/33199487
#SPJ12
BrF5 oxidation number
Answers
Answer:
+5
Explanation:
hope this helps! :)
choose the following true statement. group of answer choices a triple bond may consist of one sigma bond and two pi bonds or of two sigma bonds and one pi bond. a carbon atom involved in only single bonds may not be sp2 hybridized. a pi bond can hold 4 electrons, two above and two below the sigma-bond axis. a sigma bond is a bond resulting from side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals. a pi bond is a bond resulting from side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals.
Answers
A triple bond may consist of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
Sigma bonds are the most powerful kind of covalent chemical bond. they're fashioned by way of head-on overlapping among atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most surely described for diatomic molecules the usage of the language and equipment of symmetry businesses
Sigma bond is a covalent bond formed by overlap of atomic orbitals and hybrid orbitals along the bond axis. The sigma bond in the a hydrogen molecule is formed by overlap of a pair of 1s orbitals, one from each hydrogen atom.
The pi bond is the same as that of the p orbital when seen down the bond axis.
A pi bond is a weaker chemical covalent bond than a sigma bond.
Learn more about sigma bond here:- https://brainly.com/question/26033706
#SPJ4
Which is a mixture
H20
Salad
Table salt
Answers
Answer:
salad is a mixture this is the answer of the question
please mark ne has a brainliest
how much volume does 3 moles of gas occupy at standard temperature and pressure?
Answers
3 moles⋅22.4 L/1 mole=67.2 L Likewise, 0.5 moles of gas will occupy half the volume 1 mole occupies 0.5 moles⋅22.4 L/1 mole = 11.2 L
Standard Temperature and Pressure conditions imply a temperature of 273.15 K and a pressure of 1 atm. When these conditions are met, 1 mole of any ideal gas occupies exactly 22.4 L. Keep in mind that ideal gas particles are assumed to have no volume of their own, that's why, for example, at STP 1 mole of helium gas will occupy the same volume as, say, 1 mole of chlorine gas.
However, as you can see in the picture, the two gases will have different masses because of the difference in their molar mass. The balloon filled with helium will weigh less than the one filled with chlorine, despite the fact that they occupy the same volume.
So, if 1 mole occupies 22.4 L, the immediate conclusion is that a bigger number of moles will occupy more than 22.4 L, and a smaller number of moles will occupy less than 22.4 L.
In your case, 3 moles of gas will occupy 3 times more volume than 1 mole of gas.
3 moles⋅ 22.4 L/1 mole=67.2 L
Likewise, 0.5 moles will occupy half the volume 1 mole occupies
0.5 moles⋅ 22.4 L/1 mole=11.2 L
Learn more about gas here: https://brainly.com/question/29197891
#SPJ4
A 25.0-mL sample of 0.35 M HCOOH is titrated with 0.20 M KOH. What is the pH of the solution after 25.0 mL of KOH has been added to the acid?
Ka = 1.77 × 10-4
Answers
The pH of the solution after 25.0 mL of KOH has been added to the acid is 10.37.
HCOOH is a weak acid that reacts with KOH (a strong base) to form the HCOO⁻ ion and water:
HCOOH + KOH → HCOO⁻ + H₂O
The balanced chemical equation shows that the stoichiometric ratio of HCOOH to KOH is 1:1, so 25.0 mL of 0.20 M KOH corresponds to the same amount of moles of HCOOH. This means that 25.0 mL of the original 0.35 M HCOOH solution has reacted with the 25.0 mL of 0.20 M KOH solution.
moles of HCOOH remaining = moles of HCOOH initially - moles of KOH added
moles of HCOOH initially = 0.35 mol/L × 0.0250 L = 0.00875 mol
moles of KOH added = 0.20 mol/L × 0.0250 L = 0.00500 mol
moles of HCOOH remaining = 0.00875 mol - 0.00500 mol = 0.00375 mol
The concentration of the remaining HCOOH is:
[ HCOOH ] = moles of HCOOH remaining / volume of solution remaining
= 0.00375 mol / (25.0 mL + 25.0 mL)
= 0.075 M
Now we can use the expression for the dissociation constant of HCOOH to calculate the pH of the solution:
Ka = [ H⁺ ][ HCOO⁻ ] / [ HCOOH ]
We can assume that the HCOO⁻ ion behaves as a weak base and calculate its concentration using the equation:
[ HCOO⁻ ] = Ka / [ HCOOH ]
[ HCOO⁻ ] = (1.77 × 10⁻⁴) / 0.075 ≈ 2.36 × 10⁻³ M
Now we can use the equation for the ionization of water to calculate [ H⁺ ]:
Kw = [ H⁺ ][ OH⁻ ]
1.00 × 10⁻¹⁴ = [ H⁺ ][ 2.36 × 10⁻³ ]
[ H⁺ ] = 4.24 × 10⁻¹¹ M
Therefore, the pH of the solution is:
pH = -log[H⁺] ≈ 10.37
Learn more about solution PH here:
https://brainly.com/question/26424076
#SPJ11
which of the following is an example of pure chemistry? a. an analytical chemist determining the best way to filter contaminants out of drinking water b. a biochemist studying how the ribosome (a large complex of proteins) works c. an inorganic chemist developing a new alloy for use on ships that is resistant to corrosion by sea water d. an organic chemist working to synthesize a new cancer drug
Answers
a biochemist investigating the function of the massive protein complex known as the ribosome
What action might a chemical analyst take?
In industry, academia, and government, analytical chemists are used in many facets of chemical research. They conduct fundamental laboratory research, create procedures and products, create analytical instrumentation, teach, and engage in marketing and legal activities.
What are the four types of chemical analytical techniques?
Analytical chemistry is important in four main areas since it is used in many different scientific fields. These fields include chromatography, potentiometry, acid-base techniques, and spectroscopy.
To know more about Biochemist
Visit:
https://brainly.com/question/8167734
The chemical properties of an element are determined by which
particle of an atom?
electron
b
nucleus
оооо
proton
neutron
Answers
The chemical properties of an element are determined by which particle of an atom?
\(\longrightarrow{\green{c.\:proton}}\)
Explanation:
The chemical properties of an element are determined by the subatomic particle known as a proton. The number of protons in an atom is called its atomic number ( Z ).
\(\large\mathfrak{{\pmb{\underline{\orange{Mystique35 }}{\orange{♡}}}}}\)
how do ions form bonds, and describe the structure of the resulting compound.
Answers
Answer:
Electrons are transferred between atoms together in the ionic compound. The ions are arranged in a regular repeating pattern in an ionic crystal
Explanation:
Ions electrostatically attracts its counter ions and forms the ionic bond between these ions. The structure of ionic compounds depends on the number of atoms and bonded pair of electrons.
What is ionic bonding ?Ionic bonds are formed between metals and non-metals. Metals are electron rich and easily loss one or more electrons to the electron deficient non metals.
The loss of electrons make the atom forms a positive ion called cations. The gain of electrons make the formation of anions or negative ions. These positive ions and negative ions attracts electrostatically and forms ionic bond between them.
The structure of ionic compounds depends on the number of bonded atoms, size, presence of lone pairs etc. In solution ionic compounds exists as separate ions.
Find more on ionic bonding :
https://brainly.com/question/11527546
#SPJ2
Metallic bonding allows relatively free movement of electrons between atoms. This bonding results in the malleability of substances. A sample of which substance would most likely exhibit malleability?.
Answers
Answer: Copper
Explanation: A material's ability to form thin sheets under pressure by hammering or rolling is called Malleability.Metallic bond is a term used to describe the collective sharing of a sea of valence electrons between several positively charged metal ions.Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions.A strong metallic bond will be the result of more delocalized electrons, which causes the effective nuclear charge on electrons on the cation to increase, in effect making the size of the cation smaller. Metallic bonds are strong and require a great deal of energy to break, and therefore metals have high melting and boiling points
find more:- https://brainly.com/question/29404080?referrer=searchResults
#SPJ4
Joshua uses his thermometer (experimental value) and finds the boiling point of ethyl alcohol to be 75°C 75 ° C . The accepted value of ethyl alcohol is 80°C 80 ° C . What is his percent error?
Answers
75-80 = 5 = .0625 X 100 = 6.25%
80 80
12. Particles in the air move
a.
in an organized fashion
b. freely
C. slowly
d.
without hitting one another
Answers
What else is produced during the combustion of propane, C3H8?
C3 H8 + 502 → 3CO2 + 4_______
A) H20
B) C3H8
C) O2
D) C3H8O2
Answers
Answer:
H2O
option a is correct
4H2O is 8 H.
What is the energy of a photon that, when absorbed by a hydrogen atom, could cause an electronic transition from the n=2 state to the n=5 state?
Answers
To determine the energy of a photon required for an electronic transition from the n=2 state to the n=5 state in a hydrogen atom, we can use the formula for the energy of a photon:
E = ΔE = hc/λ
Where:
- E is the energy of the photon
- ΔE is the change in energy between the initial and final states
- h is Planck's constant (approximately 6.626 x 10^-34 joule-seconds)
- c is the speed of light (approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second)
- λ is the wavelength of the photon
The energy difference between two energy levels in a hydrogen atom is given by the Rydberg formula:
ΔE = Rh * (1/n_f^2 - 1/n_i^2)
Where:
- ΔE is the change in energy
- Rh is the Rydberg constant (approximately 2.18 x 10^-18 joules)
- n_f is the final energy level (n=5 in this case)
- n_i is the initial energy level (n=2 in this case)
Substituting the values into the Rydberg formula:
ΔE = Rh * (1/5^2 - 1/2^2)
= Rh * (1/25 - 1/4)
= Rh * (4/100 - 25/100)
= Rh * (-21/100)
≈ -0.0218 * Rh
Now, we can substitute this change in energy value into the energy formula for the photon:
E = hc/λ = -0.0218 * Rh
Rearranging the equation to solve for λ:
λ = hc / E
Substituting the values for h, c, and E:
λ = (6.626 x 10^-34 joule-seconds * 3 x 10^8 meters per second) / (-0.0218 * Rh)
Calculating this expression will give us the wavelength of the photon required for the electronic transition.
¿Qué tipo de Inter conversión existe en una celda galvánica o en una celda electrolítica? a) de energía química a energía eléctrica y viceversa b) de energía eléctrica a energía química c) de energía química a energía eléctrica d) de energía lumínica a energía eléctrica
Answers
Answer:
Opción a)
Explanation:
En este caso, vamos a explicartelo descartando opciones. Para empezar el proceso que existe en una celda galvánica o electrolítica, es lo que uno llama un proceso de Electroquímica, y permite manipular y usar la energía electrica para generar una reacción.
En este caso, yo tengo por ejemplo una celda galvánica con dos componentes como hierro y cobre conectados mediante una celda. El proceso de reacción entre ellos es lo que ayudará a que se genere energia electrica y esto, encendería un bombillo de luz. También puede ocurrir lo contrario. Con electricidad, se genera una reacción química. En estos casos, se genera una reacción de tipo REDOX (Oxido reducción).
Tomando en cuenta esto, la respuesta correcta sería la opción a). Veamos por que las otras opciones no son:
b) Energía eléctrica a química
Esta opción es falsa, porque estaría supeditando que una reacción solo puede darse por medio de una manipulación de la energía electrica y en las celdas galvánicas no ocurre eso, sino al revés.
c) Energía química a eléctrica
Falsa, porque es igual que la anterior, solo está supeditado a que ocurra este tipo de reacciones y no es así.
d) energía lumínica a eléctrica
Falso porque la energía lumínica proviene tambien de la electricidad, y en el caso de una celda galvánica se genera una reacción por lo que existe otro tipo de energía.
Espero esto te ayude.
Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase exists at point F.
A) vapor + liquid
B) vapor
C) liquid
D) solid
E) supercritical fluid
Answers
Based on the given phase diagram, the point F is located in the region where the temperature is above the critical temperature and the pressure is between the critical pressure and the vapor pressure of the substance.
At this point, the substance exists in a single phase, which is a liquid. Therefore, the answer is C) liquid. It is important to note that if the point F was located above the critical temperature and above the critical pressure, the substance would exist as a supercritical fluid, which is a unique state of matter with properties of both a gas and a liquid. Therefore, the answer for the point F would be E) supercritical fluid in that case.
to know more about phase intake pls visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30887508
#SPJ11
I need help please really quick

Answers
Answer: False
Explanation:
Atoms comprise a proton with electrons that can be bonded with a neutron. Isotopes change in atomic mass due to the increase or decrease in neutrons; since neutrons always bond with protons, the number of atoms stays the same.
16. The order is for heparin 12,500 units in 250 mL D5W to infuse at 400 units per hour. STAT aPTT 6 hours after the start of the infusion, then every 6 hours. Follow heparin protocol for adjustment of dose every 6 hours.
The IV was started at 1500, and the first aPTT was done at 2100. The result was an aPTT of 55 seconds. Following the protocol, what should the nurse do next?
Answers
The aPTT result, in this case, is 55 seconds. The nurse should follow the protocol. If the aPTT is within the recommended range, the infusion dose will remain the same. Heparin is an anticoagulant drug that can prevent blood clots from forming.
aPTT is the laboratory test used to monitor heparin therapy. It is important to remember that heparin can cause bleeding if given in higher doses. For that reason, it is vital to adjust the dose of the heparin if the aPTT is outside the recommended range.Therefore, in this scenario, since the aPTT is within the recommended range, the nurse should adjust nothing. As a result, the infusion dose will remain the same as it was before. After the first aPTT is completed, the nurse should repeat it every six hours, as directed by the protocol. In conclusion, in this scenario, the nurse should do nothing since the aPTT is within the recommended range. The nurse should follow the protocol by rechecking aPTT every six hours.
To know more about anticoagulant, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31589776
#SPJ11
When 32. 3 g of magnesium nitride are used, what volume of ammonia gas will be collected at 405 k and 2. 33 atm
Answers
19.9 L volume of ammonia gas will be collected at 405 k and 2. 33 atm.
How to calculate volume of ammonia gas?The vοlume οf ammοnia gas cοllected at 405 K and 2.33 atm, when 32.3 g οf magnesium nitride (Mg₃N₂) is used, is apprοximately 19.9 L.
Tο calculate the vοlume οf ammοnia gas, we need tο use the ideal gas law equatiοn:
PV = nRT
First, we need tο determine the number οf mοles οf magnesium nitride. The mοlar mass οf Mg₃N₂ is calculated as:
Mοlar mass οf Mg₃N₂ = (3 * atοmic mass οf Mg) + (2 * atοmic mass οf N)
Mοlar mass οf Mg₃N₂ = (3 * 24.31 g/mοl) + (2 * 14.01 g/mοl)
Mοlar mass οf Mg₃N₂ ≈ 100.94 g/mοl
Number οf mοles οf Mg₃N₂ = mass / mοlar mass
Number οf mοles οf Mg₃N₂ = 32.3 g / 100.94 g/mοl
Number οf mοles οf Mg₃N₂ ≈ 0.320 mοl
Nοw, we can use the ideal gas law equatiοn tο find the vοlume οf ammοnia gas:
V = (nRT) / P
V = (0.320 mοl * 0.0821 L·atm/(mοl·K) * 405 K) / 2.33 atm
V ≈ 19.9 L
Thus, 19.9 L volume of ammonia gas will be collected at 405 k and 2. 33 atm.
Learn more about Ideal gas law here:
brainly.com/question/30458409
#SPJ4
How many molecules are contained in 1.55 moles of methane, CH 4 ?
Answers
Avogadro's law states that in one mole of a substance, there are \(6.022 \times 10^{23}\) molecules.
This means that in 1.55 moles, there are \(1.55(6.022 \times 10^{23})=\boxed{9.33 \times 10^{23} \text{( to 3 sf)}}\)
given green highlighted is user input.
calculate the actual dry mass (Kg) using the basis given
Mass Desired Wet Mix Dry basis Required (Kg) Mix (Kg) 200 120.00 MC% H20 MC% Initial of Desired Required Dry % of MC%of actual of actual (Kg) basis 7.00% 25.00% basis 25.00% 28.8 45.00% Mass wet basis
Answers
The actual dry mass can be calculated by multiplying the mass of the wet mix on a wet basis by the dry percentage.
To calculate the actual dry mass (in kg), we need to multiply the mass of the wet mix on a wet basis by the dry percentage.
1. Calculate the actual dry mass: Multiply the mass of the wet mix on a wet basis by the dry percentage. For example, if the wet mix mass on a wet basis is 120 kg and the dry percentage is 45%, the calculation would be: 120 kg * 45% = 54 kg.
To calculate the actual dry mass, multiply the mass of the wet mix on a wet basis by the dry percentage. This provides the mass of the desired dry mix (in kg).
Learn more about mass : brainly.com/question/11954533
#SPJ11
Calculate the concentrations of hydronium ion and hydroxide ion at 25°C in: (a) 0.10 M HCl, (b) 1.4 × 10–4 M Mg(OH)2, a strong base. answer with steps please
Answers
Ai. The concentration of hydronium ion, [H₃O⁺], is 0.10 M
Aii. The concentration hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] is 1×10⁻¹³ M
Bi. The concentration of hydronium, ion [H₃O⁺], is 3.57×10⁻¹¹ M
Bii. The concentration hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] is 2.8×10¯⁴ M
A. How do i determine [H₃O⁺] and [OH⁻] of 0.10 M HCl?i. The concentration of hydronium ion, [H₃O⁺] can be obtained as follow:
HCl(aq) + H₂O <=> H₃O⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
From the above equation,
1 mole of HCl contains 1 mole of H₃O⁺
Therefore,
0.10 M HCl will also contain 0.10 M H₃O⁺
Thus, the concentration of hydronium ion, [H₃O⁺] is 0.10 M
ii. The concentration of hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] can be obtained as follow:
Concentration of hydronium, ion [H₃O⁺] = 0.10 MConcentration hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] =?[H₃O⁺] × [OH⁻] = 10¯¹⁴
0.10 × [OH⁻] = 10¯¹⁴
Divide both side by 3.02×10⁻¹⁰
[OH⁻] = 10¯¹⁴ / 0.10
[OH⁻] = 1×10⁻¹³ M
Thus, concentration of hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] is 1×10⁻¹³ M
B. How do i determine [H₃O⁺] and [OH⁻] for 1.4×10¯⁴ M Mg(OH)₂?First, we shall obtain concentration hydroxide ion, [OH⁻]. Details below:
Mg(OH)₂(aq) <=> Mg²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻(aq)
From the above equation,
1 mole of Mg(OH)₂ is contains 2 mole of OH⁻
Therefore,
1.4×10¯⁴ M Mg(OH)₂ will contain = 1.4×10¯⁴ × 2 = 2.8×10¯⁴ M OH⁻
Thus, concentration hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] is 2.8×10¯⁴ M
Now, we shall obtain the concentration of hydronium, ion [H₃O⁺]. Details below:
Concentration of hydroxide ion, [OH⁻] = 2.8×10¯⁴MConcentration of hydronium, ion [H₃O⁺] = ?[H₃O⁺] × [OH⁻] = 10¯¹⁴
[H₃O⁺] × 2.8×10¯⁴ = 10¯¹⁴
Divide both side by 2.8×10¯⁴
[H₃O⁺] = 10¯¹⁴ / 2.8×10¯⁴
[H₃O⁺] = 3.57×10⁻¹¹ M
Thus, the concentration of hydronium, ion [H₃O⁺], is 3.57×10⁻¹¹ M
Learn more about hydroxide ion concentration, [OH⁻]:
https://brainly.com/question/19800885
#SPJ1
A compound found in the athletes urine had a percent composition of 80.8% carbon, 8.97% hydrogen and 10.3% oxygen. What is the Empirical formula of the compound? What is the molecular formula of the compound if the molar mass of the compound is 312g/mol?
Answers
Answer:
C21H2802
Explanation:
C=12g/mol
H=1g/mol
O=16g/mol
Part (C) of compound-80.18%
(0.8018 x 312)/12=21
Part (H) of compound-8.97%
(0.897 x 312)/1=28
Part (O) of compund-10.3%
(0.103 x 312)/16 = 2
Therefore the emp. formula is C12H28O2